VIDEO: Examinación de niños usando el video-Impulso Cefálico (vHIT)
Published on: December 16, 2015
El vHIT se realiza fácil y confiable con los niños.
La evaluación vestibular en niños muchas veces puede ser complicado si el medico no tiene acceso a una silla giratoria o VEMP. El uso del recientemente creado vHIT ofrece un protocolo simple, extremadamente seguro, no invasivo y de alta sensibilidad para evaluar niños rápidamente. El uso del VNG, particularmente calóricas es una mala opción cuando comparado al vHIT. Calóricas no siempre son toleradas por los niños pequeños, tienen sensibilidad limitada (.0003 Hz), no proveen el estado de descompensación, y se ha escrito en literatura que induce la migraña en algunos pacientes.
Estudio de Caso: Niña de siete años con dolor de cabeza, mareos y nausea casi a diario y con vomito ocasional cuando el dolor de es cabeza es severo. Otorrinolaringólogo Pediátrico la refiere al nuestro Instituto. Hay historia materna de migraña y la niña sufre de intolerancia al movimiento (transporte). Además de la historia pre y post-natal hay historia negativa otológica.
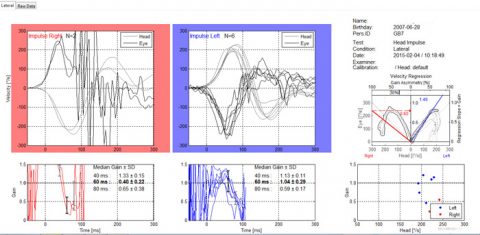
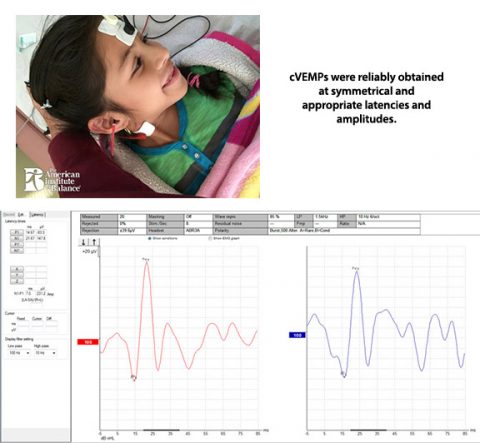
El protocolo pediátrico del AIB para un niño de esta edad incluye: El examen Gans Sensory Organization Performance (Gans SOP), silla rotatoria, VEMP, VOG con posiciones y vHIT. En el video y la tabla de resultado se puede ver que todos los exámenes estuvieron en el rango normal de los parámetros. El vHIT junto con la valoración de balance/postural Gans SOP o CTSIB hubiera proporcionado una cantidad de datos significativos al no haber estado disponible las otras pruebas para sugerir que no había participación laberíntica aguda o activa. Sin embargo, es preferible siempre que sea posible realizar el cVEMP, particularmente con los pacientes que sufren de migraña. La probabilidad más prominente es un patrón de migraña vestibular inducida por la edad. La niña será referida a un neurólogo pediátrico para consulta y manejo.
The vHIT is easily and reliably performed with children.
Referencias:
1. Gans RE, Evaluation and Management of Vestibular Function in Infants and Children with Hearing Loss, (2014), In Madell and Flexer, Pediatric Audiology- Diagnosis, Technology, and Management, Thieme, NY.
2. Colagiorgio, P., et.al., A new tool for investigating the functional testing of the VOR, Frontiers in Neurology (2013), vol. 4, Article
3. Murdin, L. , Davies, R. A., Bronstein, A. M., Vertigo as a migraine trigger, (2009) Neurology, 73 p.638-642